Services
Phacoemulsification Cataract Surgery
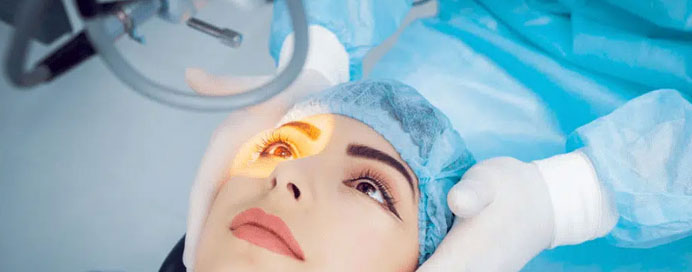
Best Treatment For Lasik Eye Surgery in Vile Parle,Andheri
Phacoemulsification cataract surgery is a modern and widely used technique for removing cataracts, which are cloudy formations in the eye's natural lens that impair vision. The procedure involves making a small incision in the cornea, through which an ultrasonic probe is inserted. This probe emits high-frequency sound waves that emulsify, or break apart, the cloudy lens into tiny fragments. These fragments are then suctioned out of the eye, leaving an empty capsule. A foldable artificial intraocular lens (IOL) is then inserted into this capsule to restore clear vision. Phacoemulsification is minimally invasive, requires a small incision, and typically results in a quick recovery with fewer complications compared to traditional cataract surgery methods.
